| 8255 functions
( General overview )
|
|||
|
General The Intel 8255A is a general purpose programmable I/O device which is
designed for use with all Intel and most other microprocessors. It provides
24 I/O pins which may be individually programmed in 2 groups of 12 and
used in 3 major modes of operation. The 8255 is a 40 pin integrated circuit (IC), designed to perform a variety of interface functions in a computer environment. The 8255 wasn't originally designed to be connected to the Z80. It was manufactured by Intel for the 8080 microprocessor. |
|||
|
PIN configuration
|
|||
|
Block diagram 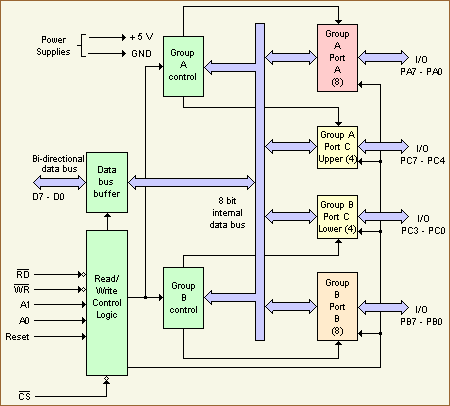
Two control groups, labeled group A control and group B control define how the three I/O ports operate. There are several different operating modes for the 8255 and these modes must be defined by the CPU writing programming or control words to the device 8255. The line group of port C consists of two 4 bit ports. One of the 4 bit group is associated with group A control and the other 4 bit group with group B control device signals. The upper 4 bits of port C are associated with group A control while the lower 4 bits are associated with group B control. The final logic blocks are read/write control logic and data bus buffer. These blocks provide the electrical interface between the Z80 and the 8255. The data bus buffer buffers the data I/O lines to/from the Z80 data bus. The read/write control logic routes the data to and from the correct internal registers with the right timing. The internal path being enabled depends on the type of operation performed by the Z80. The type of operation can be I/O read or I/O write. |
|||
|
Control Word Register Before going to discuss the detailed description about the usage of the 8255 in the MZ-700, you should see the bit definitions of the 8255 control word register (port $E003 of the MZ-700). If bit 7 of the control word is a logical 1 then the 8255 will be configured. See the picture of the practicable configurations: 
If bit 7 of the control word is a logical 0 then each bit of the port C can be set or reset. See the picture of the practicable possibilities: 
Examples: Go to page "Memory mapped I/O" to download the complex datasheet of the 8255. |
